Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses: Pros, Cons, and Use Cases
In the world of networking and internet connectivity, IP addresses are fundamental. They serve as unique identifiers for devices on a network, facilitating seamless communication. There are two primary types of IP addresses: dynamic and static. Understanding their differences, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases is crucial for both individuals and businesses navigating the digital world.
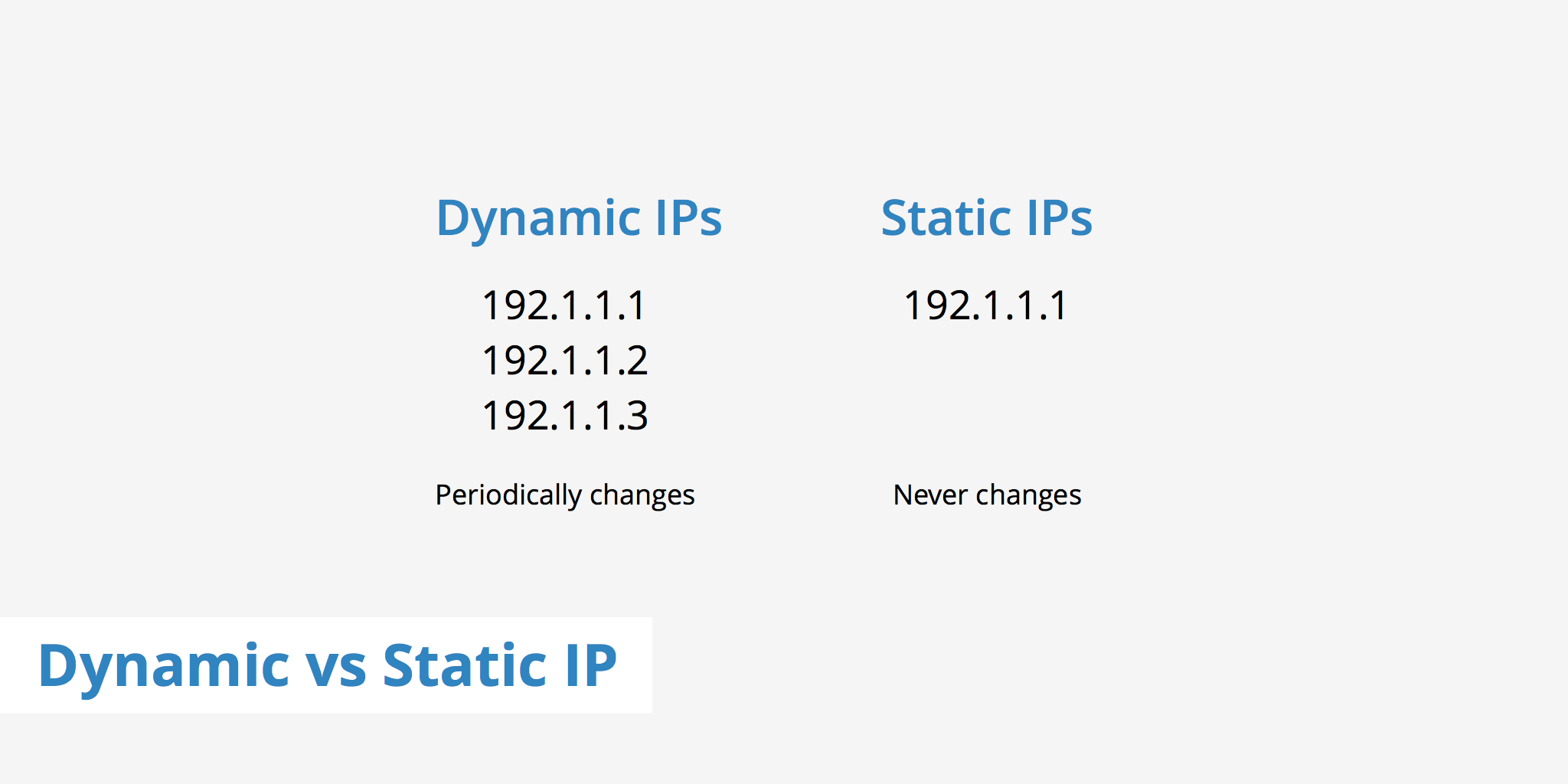
What are Dynamic and Static IP Addresses?
- Dynamic IP addresses are those that are assigned to a device for a specific session. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) automatically assigns these addresses using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Each time the device connects to the internet, it may receive a different IP address.
- Static IP addresses, in contrast, are permanent. They are manually assigned and don't change over time. These IPs are typically configured by an IT professional and remain constant regardless of network or device restarts.
Pros and Cons of Dynamic IP Addresses
Pros ✅
- Cost-Effective: Dynamic IPs are generally less expensive than static IPs, as they require less management and oversight from the ISP.
- Easy Management: Since the allocation is automatic, they require minimal management, making them user-friendly for non-technical users.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: The changing nature of dynamic IP addresses provides a layer of privacy and security, making it more difficult for malicious entities to track or attack a constantly changing target.
Cons ❌
- Inconsistency: The lack of a permanent address can be problematic for hosting servers or devices that require remote access.
- Connectivity Issues: Some online services and gaming platforms that require IP verification might face connectivity issues due to the changing IP.
Pros and Cons of Static IP Addresses
Pros ✅
- Reliability: Static IPs provide a consistent point of contact for devices, which is crucial for servers hosting websites, VPNs, or email servers.
- Necessary for Certain Applications: Some advanced internet services, like setting up a file server or remote desktop access, require a static IP to function correctly.
- Easier to Diagnose Problems: Network issues can be more straightforward to diagnose with static IPs as the address remains constant.
Cons ❌
- Cost: Static IP addresses are typically more expensive, as they require more management from the ISP.
- Security Risks: If not properly secured, static IPs can be more vulnerable to cyber attacks since the attacker can consistently find that IP online.
- Complex Configuration: They require manual setup, which can be daunting for those without technical expertise.
Use Cases for Dynamic and Static IP Addresses
Dynamic IP Addresses:
- Ideal for casual internet users at home or small businesses not relying on web or file servers.
- Suitable for devices that don't need to maintain the same IP address, like mobile phones, tablets, and laptops used for general browsing.
Static IP Addresses:
- Essential for hosting websites, email servers, or VPN services, where a constant address is necessary for accessing the services.
- Preferred for online gaming servers or VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services, where a stable connection is critical.
- Useful for businesses with remote access needs, where employees need to access work computers or servers from different locations.
Conclusion
Choosing between dynamic and static IP addresses depends largely on the specific needs and use cases of the user or organization. For most home users and small businesses, dynamic IPs offer a cost-effective and low-maintenance solution. However, for those hosting servers or requiring stable, remote access, static IPs are the way to go. Understanding the pros and cons of each helps in making an informed decision that aligns with your connectivity requirements and overall digital strategy.